Architecture Overview
During the workshop we will use a calculator app to get familiar with Kubernetes.
Overall architecture
The app basically consists of three services: the backend, a frontend and the database.
- The user accesses the frontend to let the application evaluate an expression.
- The frontend uses the backend to calculate the result of the calculation.
- The backend can use an external database to store a history of calculations.
- The backend and frontend can be scaled up and down to handle increased load.
Frontend service
The frontend is a UI to enter calculations and view the result. It is also possible to view a history of all calculations.
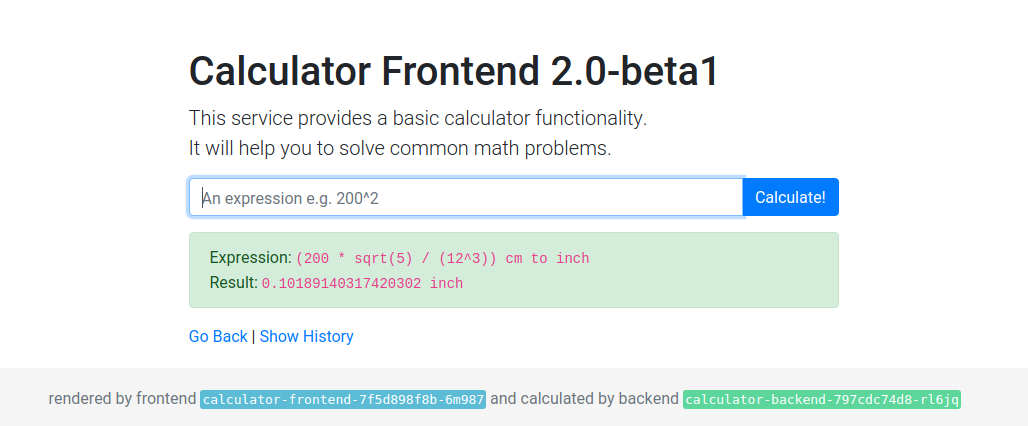
- The service is implemented in Node.js and Typescript.
- It uses React with server-side rendering to generate the HTML page.
- It communicates with the backend using REST and JSON.
- It is already packaged with Docker and published in a registry.
Images
These images can be used to run a calculator frontend on Kubernetes.
| Image | Description |
|---|---|
quay.io/kubernetes-workshop/calculator-frontend:v1 |
Version 1 with calculation functionality |
quay.io/kubernetes-workshop/calculator-frontend:v2 |
Version 2 with a UI to show the history |
Configuration options
The frontend service needs to know how to reach the backend service, this is done with an environment variable.
| Environment variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
CALCULATOR_BACKEND_BASE_URL |
- |
Example could be http://backend.local:8080 |
Backend service
The backend is a service that returns the result for a mathematical expression. It stores a history of expressions and their results.
- The service is implemented in Node.js and Typescript.
- It uses Express to provide a REST API.
- The expressions are parsed and calculated using Math.js.
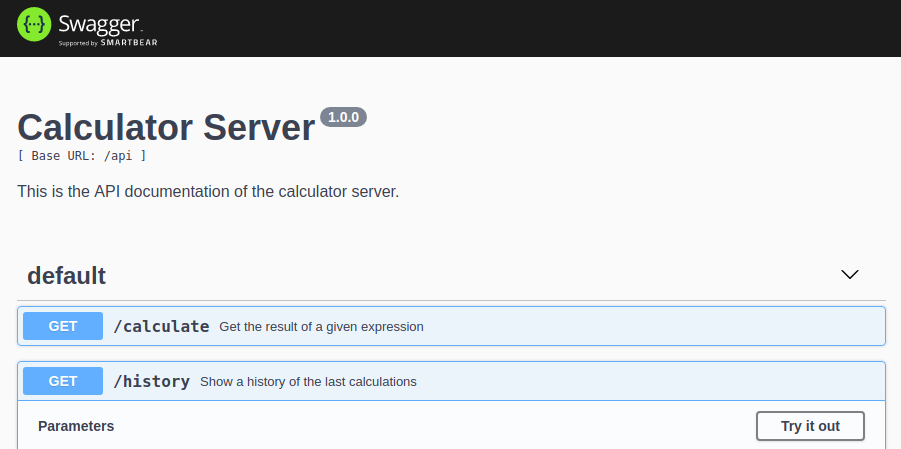
- It provides a graphical UI to test the REST API using Swagger, it is served under
/. - It provides an endpoint
GET /calculateto calculate the result of a given expression. - It provides an endpoint
GET /historyto get a list of previous calculations. - It uses a database to store a history of previous calculations.
- By default it is stored in an internal SQLite database.
- It is possible to store the history in an external PostgreSQL database.
Known bugs
The service has a known bug. It will crash when an expression can’t be parsed. This must be taken into account when running the service. During the tutorial we will implement mechanisms to automatically recover from crashes of the service.
Images
These images can be used to run a calculator backend on Kubernetes.
| Image | Description |
|---|---|
quay.io/kubernetes-workshop/calculator-backend:v1 |
The backend with all features |
Configuration options
The backend service can be configured to store the calculation history in a PostgreSQL database. Therefore it must be configured where the service can find the database.
| Environment variable name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
PG_HOST |
- |
The hostname where the PostgreSQL server can be found |
PG_PORT |
5432 |
The port where the PostgreSQL server listens |
PG_USER |
postgres |
The user used for authentication against the database |
PG_PASS |
postgres |
The password used for authentication against the database |
PG_DB |
calculator |
The database name used to store the history |
A PostgreSQL connection is only used when the PG_HOST variable is configured. Otherwise SQLite is used.